Backpropagation Neural Network
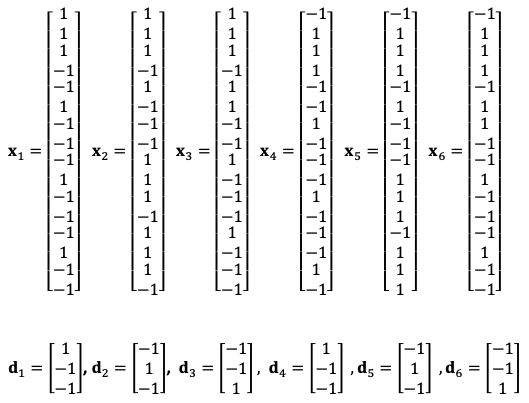
This is an example of a simple symbol recognition problem with three letters T, G and F, in an original form and in a shifted form. The 6 input vectors $x_1, x_2, x_3, x_4, x_5, x_6$ and the corresponding target vectors $d_1, d_2, d_3$ in the training set are:
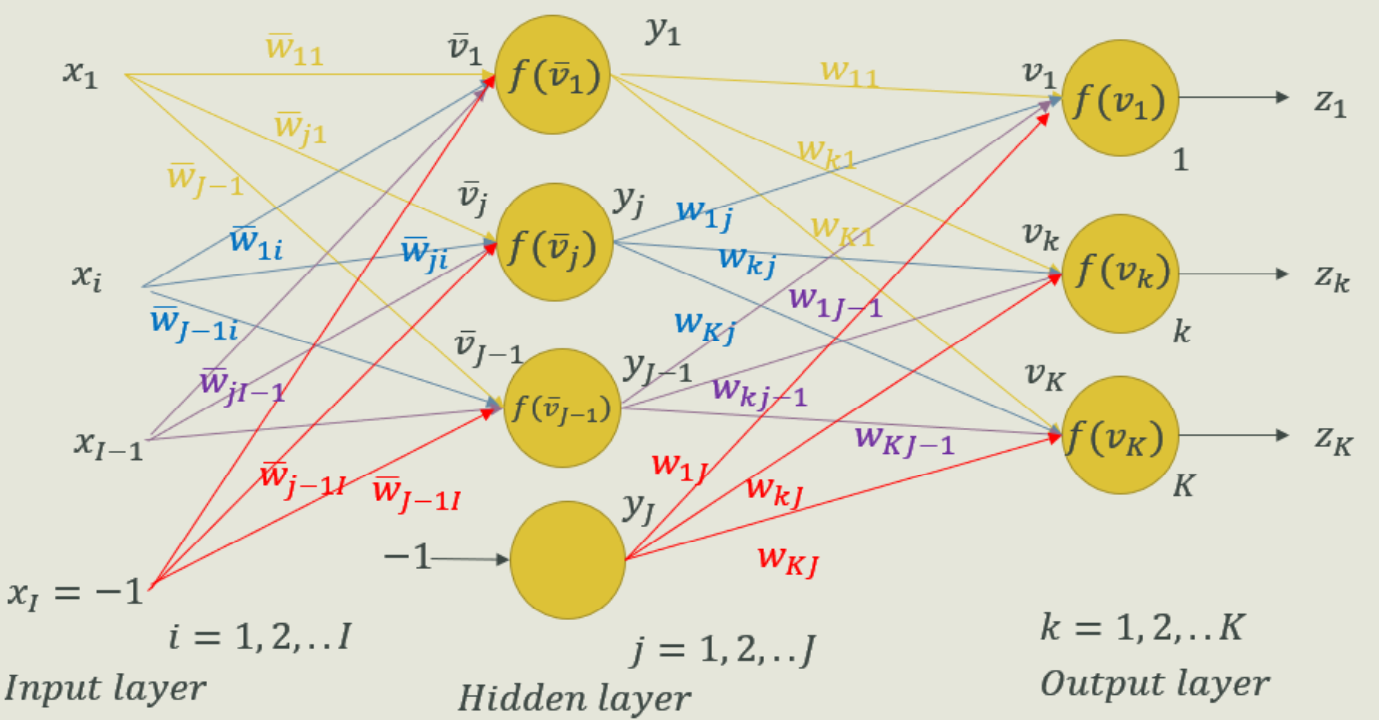
We will assume that the network has one hidden layer with 3 neurons and all continuous perceptrons use the bipolar activation function $f(v)=\frac{1-e^{-v}}{1+e^{-v}}$. Note that the trained network should have 17 input nodes, 3 hidden neurons, and 3 output neurons due to necessary augmentation of inputs and hidden layer by one fixed input. We will assign −1 to all augmented inputs. The resulting network has the following form:
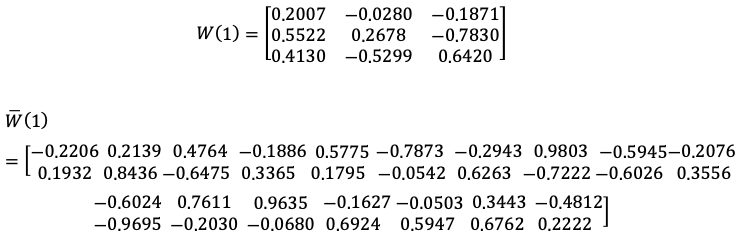
The learning constant $n = 0.25$, and the initial random weights for the output and hidden layers are:
Setup
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Constants
## input vectors
x_fig = np.array([[1,1,1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1],
[1,1,1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,1,1,-1,1,1,1,-1],
[1,1,1,-1,1,1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1],
[-1,1,1,1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,-1],
[-1,1,1,1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,1,1,-1,1,1,1],
[-1,1,1,1,-1,1,1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1]])
x = np.append(x_fig, -1*np.ones((6,1)), axis=1)
## Target vectors
d = np.array([[1,-1,-1],
[-1,1,-1],
[-1,-1,1],
[1,-1,-1],
[-1,1,-1],
[-1,-1,1]])
## Learning rate
n = 0.25
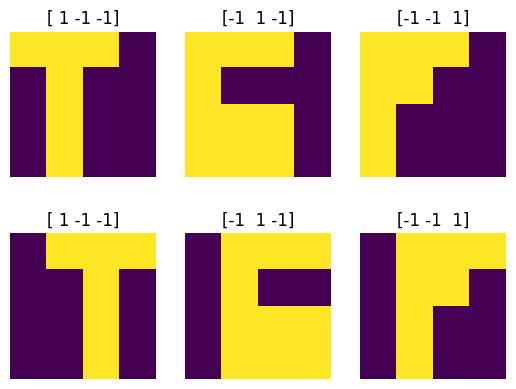
# Visualize the data
# plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
for i in range(6):
ax = plt.subplot(2, 3, i + 1)
plt.imshow(x_fig[i].reshape(4,4))
plt.title(str(d[i]))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
# Variables
## Initial random output layer weight matrix W1
w = np.array([[0.2007, -0.0280, -0.1871],
[0.5522, 0.2678, -0.7830],
[0.4130, -0.5299, 0.6420]])
## Initial hidden layer weight matrix W_1
wp = np.array([[-0.2206, 0.2139, 0.4764, -0.1886, 0.5775, -0.7873,
-0.2943, 0.9803, -0.5945, -0.2076, -0.6024, 0.7611,
0.9635, -0.1627, -0.0503, 0.3443, -0.4812],
[0.1932, 0.8436, -0.6475, 0.3365, 0.1795, -0.0542,
0.6263, -0.7222, -0.6026, 0.3556, -0.9695, -0.2030,
-0.0680, 0.6924, 0.5947, 0.6762, 0.2222]])
# activation function and derivative of the activation function
## Bipolar function
def bipolar(v):
return ((1-np.exp(-v))/(1+np.exp(-v)))
## Derivative of the bipolar function
def dbipolar(v):
return 0.5*(1-v**2)
Solution
# Multilayer Neural Network:
## Initial output layer weight matrix W
w = np.array([[0.2007, -0.0280, -0.1871],
[0.5522, 0.2678, -0.7830],
[0.4130, -0.5299, 0.6420]])
## Initial hidden layer weight matrix W_1
wp = np.array([[-0.2206, 0.2139, 0.4764, -0.1886, 0.5775, -0.7873,
-0.2943, 0.9803, -0.5945, -0.2076, -0.6024, 0.7611,
0.9635, -0.1627, -0.0503, 0.3443, -0.4812],
[0.1932, 0.8436, -0.6475, 0.3365, 0.1795, -0.0542,
0.6263, -0.7222, -0.6026, 0.3556, -0.9695, -0.2030,
-0.0680, 0.6924, 0.5947, 0.6762, 0.2222]])
wh = [w]
wph = [wp]
cr = []
for j in range(200):
e = 0
for i in range(len(x)):
# Hidden layer
vp = np.dot(wp, x[i])
y = bipolar(vp)
dy = dbipolar(y)
# Output layer
v = np.dot(w, np.append(y, -1))
z = bipolar(v)
dz = dbipolar(z)
r = d[i]-z
delta = np.multiply(r, dz)
dp = np.multiply(np.dot(delta, w[:,0:2]), dy)
deltawp = n*np.dot(np.array([dp]).T, np.array([x[i]]))
# Update weights
w = w + n*np.dot(np.array([delta]).T, np.array([np.append(y, -1)]))
wp = wp + deltawp
# Update weights record
wh.append(w)
wph.append(wp)
p = np.sum(0.5*(r**2))
e += p
cr.append(e)
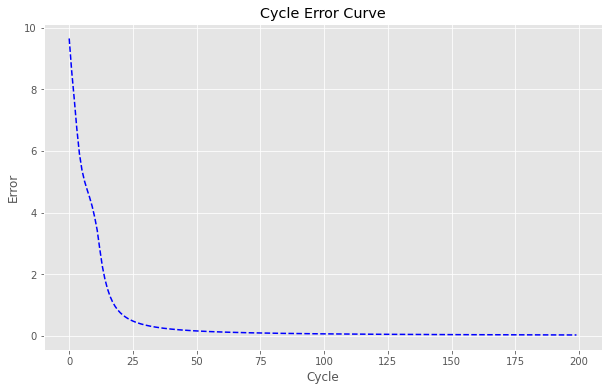
Cycle error curve:
# Cyle Error curve
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [10, 6]
plt.style.use('ggplot')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(range(len(cr)), cr,
linestyle='--',
color='blue')
ax.set_ylabel('Error')
ax.set_xlabel('Cycle')
ax.set_title('Cycle Error Curve')
plt.show()
Prediction
The test character below, has the following feature input vector:
x1_2_fig = np.array([1,1,1,-1,-1,1,1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,1,-1])
x1_2 = np.array([1,1,1,-1,-1,1,1,-1,-1,1,-1,-1,-1,1,1,-1,-1])
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [5, 5]
plt.style.use('default')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.imshow(x1_2_fig.reshape(4,4))
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Test Character')
plt.show()

With the current set of weigths, the new input image will be classified as a T with d = [1, -1, -1]
# Classification using final weights
vp = np.dot(wp, x1_2)
y = bipolar(vp)
v = np.dot(w, np.append(y, -1))
z = bipolar(v)
print(z)
print(np.round(z))
[ 0.9352934 -0.94743224 -0.95992767]
[ 1. -1. -1.]
